A customer data platform (CDP) is an advanced customer data management solution consisting of a centralized customer database platform with the ability to ingest, integrate, manage, activate, orchestrate, and deliver customer data to other technology solutions to personalize the customer experience (CX) at scale.
According to Gartner, a CDP is defined as a software application that supports marketing and customer experience use cases by unifying a company’s customer data from marketing and other channels. CDPs optimize the timing and targeting of messages, offers, and customer engagement activities, and enable the analysis of individual-level customer behavior over time.”
Customer data platform software collects and integrates all forms of customer data to create a unified customer profile (also known as a single customer view (SCV). This unified view can then be used to align all business efforts around a single source of customer truth. Customer data platform solutions can collect consumer behavior, demographic, and transactional data to track and analyze customer interactions with your organization.
Customer data platforms were created to manage first-party, second-party, and third-party data from multiple disparate channels and unite customer-centric efforts across marketing, sales, and customer service. CDP platforms also give brands the ability to manage data and consent centrally, which helps them stay in compliance with emerging data privacy regulations.
Just Released: The Forrester Wave™: Customer Data Platforms for B2B, Q3 2025. Access your complimentary copy, courtesy of Treasure Data, to discover the 11 B2B CDP providers that matter most and how they stack up, along with scorecards on providers’ current offering and strategies.
What Does a CDP Do?
A customer data platform improves the efficacy and efficiency of your data-driven marketing campaigns. They accomplish this by deploying CDP features like data-driven insights to tailor personalized experiences at scale.
1. Combining Structured and Unstructured Data
CDP platforms allow you to combine structured, unstructured, and semi-structured data to create a single customer view. A customer data platform can ingest data from any source, including email, social media, loyalty, and systems like enterprise resource planning (ERP), customer relationship management (CRM), and data management platforms (DMPs). Customer data platforms can analyze and segment customer profiles using rules or machine learning, perform predictive scoring, and provide customer journey orchestration.
Read More: Structured Data Vs. Unstructured Data, Explained
2. Integration with the MarTech Stack
Customer data platforms are designed to easily integrate with the rest of your technology stack through either pre-built connectors or application programming interfaces (APIs) for superior CDP analytics. This allows CDPs to function as a smart hub, making your technology stack more agile, flexible, and scalable by allowing you to plug in the best-of-breed software for your particular industry and applications.
Read More: How To Integrate A CDP Into Your MarTech Stack
3. Democratization of Data
Customer database platforms allow data to be democratized so it can be used across the entire organization (marketing, sales, customer service, support, etc.) With the right CDP features, a business can tailor its communications and build lasting relationships with customers, improving retention rates and lowering churn. Customer data platforms are also a great way to reduce customer acquisition costs while increasing retention rates.
Read More: How To Achieve Data Democratization With A CDP
4. Marketing Activation and Personalization
Customer data platforms make customer data available to other systems for campaign activation with insights that improve the customer experience across the entire omnichannel customer journey. CDP platforms allow marketers to apply advanced personalization, identify and segment key target audiences, provide relevant product and content recommendations, and implement retargeting programs.
Read More: How To Provide An Exceptional Omnichannel Customer Experience
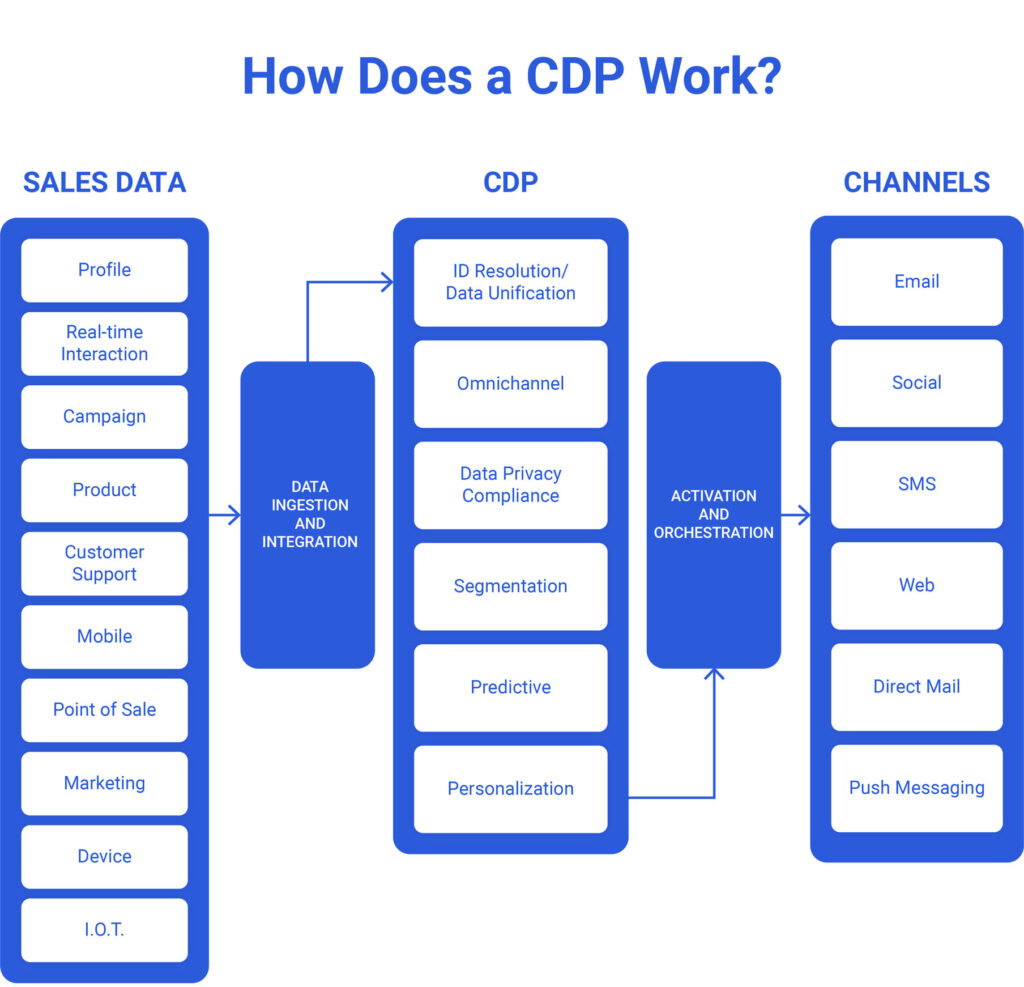
How Does a CDP Work?
A customer data platform connects to a wide range of technology platforms, data sources, and channels by using built-in connectors, SDKs, webhooks, and APIs. They ingest and integrate data from multiple disparate sources, including profile data and real-time interaction data (behavioral data, transactional data), campaign data, product data, customer support data, mobile, POS, marketing, device, and internet-of-things (IoT) data.
A customer data platform ingests and integrates those data sets to create a single unified customer profile. This integration process is called identity resolution or data unification. Customer identity resolution includes sophisticated algorithms to stitch identifiers from multiple systems, as well as automate graph creation and continuously unify data into a profile as customers engage in real-time. During the unification process, data is validated, cleaned, and de-duped to create a single customer view. Profiles are then enriched with first, second, and third-party data sources to fill in missing attributes and update other attributes with more recent information.
Customer data platform software can also analyze and segment customer profiles using rules or machine learning, perform predictive scoring, and provide journey orchestration capabilities. Some more advanced customer data platform solutions provide machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) for predictive analytics and audience segmentation. With customer journey orchestration capabilities, marketers can analyze customer interactions throughout the entire customer journey to deliver the right message, at the right time, on the proper channels.
What Are the Most Common CDP Use Cases?
The two most common CDP use cases are personalized customer experiences and targeted advertising. Other standard customer data platform features and customer data platform examples include:
- Profile Unification: Customer data records can be combined into a single 360-degree view of the customer, allowing you to do more effective personalization and reduce ineffective ad spend.
- Segmentation: CDP analytics allows marketers to identify and target high-value audiences with advanced segmentation capabilities.
- Data Unification: Customer data platform software unifies customer data into a single customer identifier that can be enriched over time, reducing duplicate profiles and inaccuracies.
- Predictive Scoring: Marketers gain the ability to predict customers’ behaviors, like who is likely to churn, purchase, click, or convert.
- Retargeting: A customer data platform can improve retargeting by connecting customer data to advertising data, creating optimized audience segments, with the ability to automate activations.
- Customer Journey Optimization: Iterative insights allow marketers to quickly test, learn, and improve marketing efforts across the entire omnichannel customer journey.
- Next-Best Action: Next-best action relies on robust customer data, analytics, and artificial intelligence (AI) to predict the next-best step sales, service, or marketing teams can take to improve the customer journey and increase conversion.
- Programmatic Advertising: CDP analytics enable you to target customers better with programmatic advertising.
- Lookalike Modeling: Advertise across channels to both known and unknown audiences with lookalike modeling based on key audience attributes.
- Customer Loyalty: Measure and predict customer loyalty, and customize communications to increase the lifetime value of your most loyal customers.
- Personalization: Once segments and audiences are identified, marketing, sales, and customer service teams can tailor messaging that speaks directly to target audiences and is delivered through the right channel, at the right time.
- Data Governance: CDP platforms enable IT and data teams to enforce data access policies and permissions across teams, ensuring that specific teams only have access to the data that they need.
- Consent Management: Customer data platform solutions can integrate with consent management solutions, allowing customer data privacy preferences to be integrated directly into unified customer profiles.
- Demand Planning and Inventory Management: With predictive CDP analytics, organizations can use customer purchase preferences, transaction data, and inventory data to predict demand and manage inventory mix across channels.
- Business Efficiency: A strong customer data foundation forms part of the blueprint for accurate attribution, making forecasting more effective.
Start with a Proof of Concept (POC)
A customer data platform is a significant investment. It is crucial to try before you buy with a proof of concept (POC).
A proof of concept is typically a smaller-scale pilot project whose goal is to demonstrate, in principle, that the idea has practical potential without requiring full development. Running a POC on any large software project is critical to ensuring it is the right fit for your business and its present and future needs. Starting with a POC will ensure that your investment remains future-proof for years to come.
In terms of a CDP platform, the POC addresses various needs, ranging from basic data ingestion to advanced marketing strategies, through data cleaning, segmentation, predictive scoring, and more.
PRO TIP: Ask every CDP vendor in your search to do a proof of concept. A POC is the best way to pressure test the technology and see if vendors can back up their claims.
What is the Difference Between a CDP and Other Data Management Solutions?
There can be some confusion over the differences and benefits of a customer data platform (CDP) versus other data management solutions, like a data management platform (DMP), a customer relationship management (CRM) platform, a data warehouse, and data lakes. While they all manage customer data in some capacity, they are all built for different purposes and have some significant variations.
What is a CDP Platform?
A customer data platform is a centralized customer database that builds unified profiles from data it collects across any number of disparate data silos. A CDP platform then delivers combined data out to other solutions in the technology stack to affect the customer experience. Continue reading for more CDP marketing examples.
What is a DMP?
A data management platform (DMP) is a software tool used primarily in advertising and marketing to build profiles of anonymous individuals, store summary data about each individual, and share their data with advertising systems.
DMPs are used to store, manage, and analyze data about ad campaigns and audiences. A DMP connects to a demand side platform (DSP) or supply side platform (SSP) to purchase ads through ad networks. A DMP ingests anonymous identifiers for your customers, matches these against third-party lists, builds a lookalike model with summary data, selects similar anonymous individuals from third-party lists, and sends those lists to advertising systems.
Read More: CDP Vs. DMP: How To Get The Best Value Out Of Customer Data
What is a CRM?
Customer relationship management platforms are designed to help organizations manage the contact information of prospects and customers. Sales channel interactions, as well as contact center and customer support calls, are also typically included as data points within a CRM.
A CRM system is used to track and record touch points along the customer journey, from pre-purchase to purchase to retention and advocacy. The system enables organizations to record customer interactions (e.g., phone calls, including dates, times, and call transcripts), as well as customer purchase history. CRM systems help organizations provide better customer service and customer experience. When used effectively, CRM systems can help retain customers and grow revenue.
Read More: CDP Vs. CRM: How To Master Your MarTech Stack
What is a Data Warehouse?
Data warehouses can receive large amounts of information from databases. Using a process called extract, transform, and load (ETL), data warehouses clean, summarize, and store data in a frozen state.
In a data warehouse, data is organized and secure, as it can’t be deleted, but without a customer data platform’s actionable capabilities, it’s less usable. A data warehouse’s rigidity means your business may find itself conforming to a data collection system rather than vice versa.
Read More: CDP Vs. Data Warehouse: What’s Best For Your Business?
What is a Data Lake?
A data lake accepts every kind of data in its original form, including unstructured or semi-structured data, like videos, PDFs, recordings, and online reviews. Given a data lake’s extract, load, transform (ELT) process, your business can use a data lake as a depository, defining organizing criteria after storing. Purposes for data lakes include using machine learning to create predictive models and forecast trends.
Choosing the Right Customer Data Platform Solution
A customer data platform may be the right choice for your organization if you need to improve the overall customer experience with data-driven insights, as well as make your marketing operations more agile and efficient.
A CDP platform can unify customer data from all your channels and disparate silos to create a single customer view that can serve as the single source of truth across your organization. This unified view allows marketing, service, and sales teams to easily analyze customer data and identify critical segments to deliver more relevant, contextual, personalized, and consistent messaging.
Want to learn more about how to choose the right customer database platform solution for your organization? Our comprehensive guide explores the key steps needed to create a successful CDP evaluation and selection process – from CDP features and CDP analytics capabilities to consider, to the questions you should ask prospective vendors to make sure you’re making the right decision. Access your copy of our guide here.